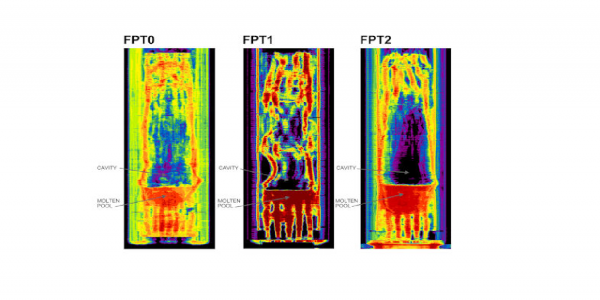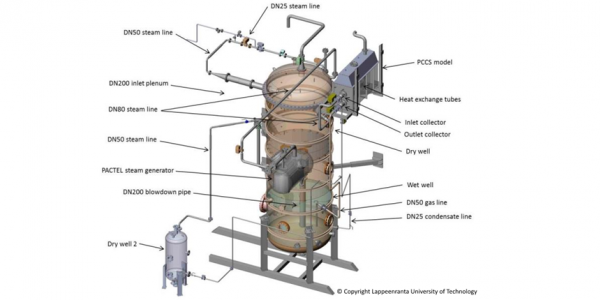
PCCS
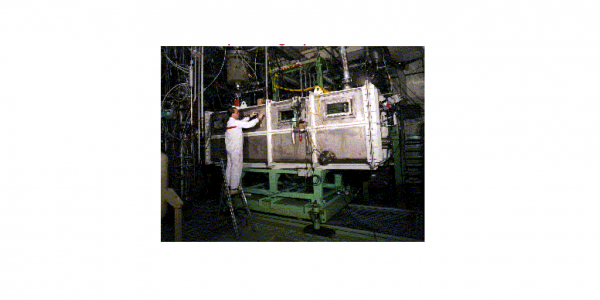
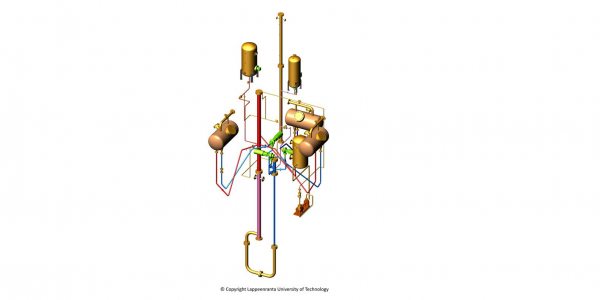
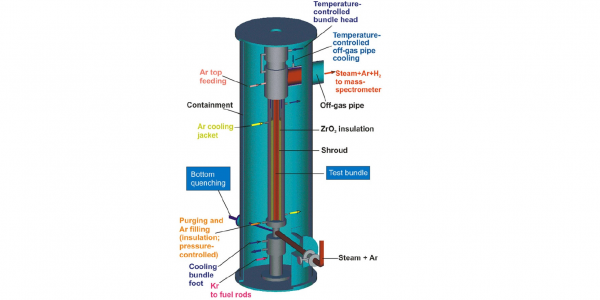
Passive Containment Cooling System (PCCS) removes residual heat from upper drywell of the containment to the liquid pool surrounding the PCCS heat exchanger. It also has an important role in mitigating the offsite dose by retention of a fission product release in the containment. The operation of the PCCS is based on density differences between the containment and water pool