PECA
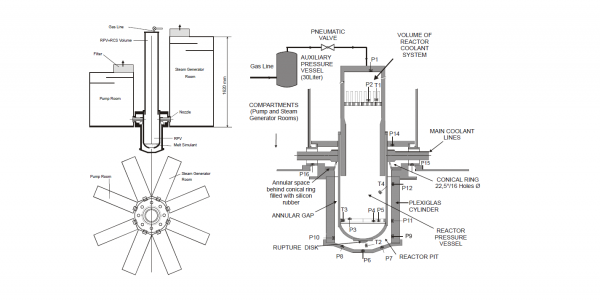
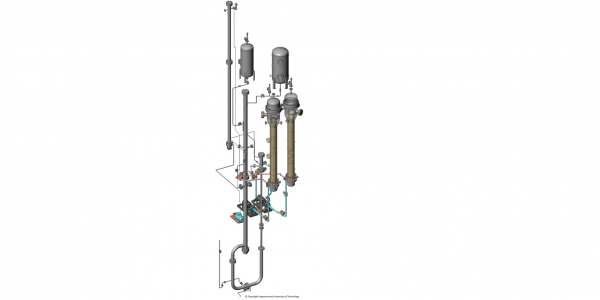
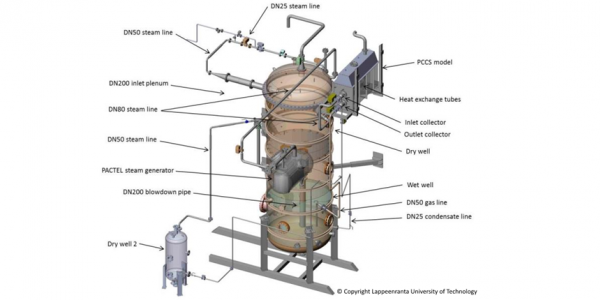
The separate effect studies of vertical steam generators have been conducted in the CIEMAT PECA facility, which was properly modified and conditioned for that purpose. The PECA facility set-up used in the SGTR separate effect tests basically consists of:
1. Two injection lines, one designed for supplying air at relatively high flow rates from a compressor, and the other for the aerosol injection.
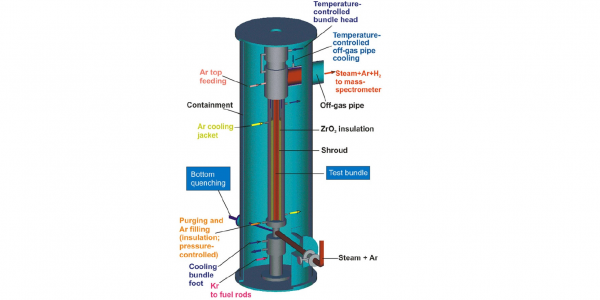
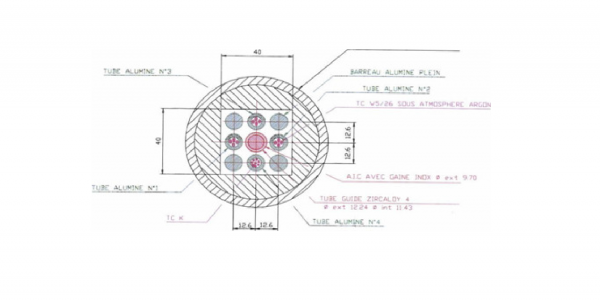
2. The vessel, containing the tube mini-bundle.
3. The associated instrumentation and sampling stations.